You are here
被子植物
Iris
EOL Text
Iris is a genus of 260–300[1][2]species of flowering plants with showy flowers. It takes its name from the Greek word for a rainbow, referring to the wide variety of flower colors found among the many species.[3] As well as being the scientific name, iris is also very widely used as a common name for all Iris species, as well as some belonging to other closely related genera. A common name for some species is 'flags', while the plants of the subgenus Scorpiris are widely known as 'junos', particularly in horticulture. It is a popular garden flower.
The often-segregated, monotypic genera Belamcanda (blackberry lily, I. domestica), Hermodactylus (snake's head iris, I. tuberosa), and Pardanthopsis (vesper iris, I. dichotoma) are currently included in Iris.
Contents
§Description[edit]
Irises are perennial plants, growing from creeping rhizomes (rhizomatous irises) or, in drier climates, from bulbs (bulbous irises). They have long, erect flowering stems which may be simple or branched, solid or hollow, and flattened or have a circular cross-section. The rhizomatous species usually have 3–10 basal sword-shaped leaves growing in dense clumps. The bulbous species have cylindrical, basal leaves.
§Flower[edit]
The inflorescences are in the shape of a fan and contain one or more symmetrical six-lobed flowers. These grow on a pedicel or peduncle. The three sepals, which are spreading or droop downwards, are referred to as "falls". They expand from their narrow base, which in some of the rhizomatous irises has a "beard" (a tuft of short upright extensions growing in its midline), into a broader expanded portion ("limb"), often adorned with veining, lines or dots. The three, sometimes reduced, petals stand upright, partly behind the sepal bases. They are called "standards". Some smaller iris species have all six lobes pointing straight outwards, but generally limb and standards differ markedly in appearance. They are united at their base into a floral tube that lies above the ovary (known as an epigynous or inferior ovary). The styles divide towards the apex into petaloid branches; this is significant in pollination.
The iris flower is of interest as an example of the relation between flowering plants and pollinating insects. The shape of the flower and the position of the pollen-receiving and stigmatic surfaces on the outer petals form a landing-stage for a flying insect, which in probing for nectar, will first come into contact with the perianth, then with the stigmatic stamens in one whorled surface which is borne on an ovary formed of three carpels. The shelf-like transverse projection on the inner whorled underside of the stamens is beneath the overarching style arm below the stigma, so that the insect comes in contact with its pollen-covered surface only after passing the stigma; in backing out of the flower it will come in contact only with the non-receptive lower face of the stigma. Thus, an insect bearing pollen from one flower will, in entering a second, deposit the pollen on the stigma; in backing out of a flower, the pollen which it bears will not be rubbed off on the stigma of the same flower.
The iris fruit is a capsule which opens up in three parts to reveal the numerous seeds within. In some species, these bear an aril.
§Taxonomy[edit]
Iris is the largest genus of the family Iridaceae with up to 300 species – many of them natural hybrids.[4] Modern classifications, starting with Dykes (1913), have subdivided them. Dykes referred to the major subgroupings as sections. Subsequent authors such as Lawrence (1953) and Rodionenko (1987) have generally called them subgenera, while essentially retaining Dykes' groupings, using six subgenera further divided into twelve sections. Of these, section Limneris (subgenus Limneris) was further divided into sixteen series. Like some older sources, Rodionenko moved some of the bulbous subgenera (Xiphium, Scorpiris and Hermodactyloides) into separate genera (Xiphion, Juno and Iridodictyum respectively), but this has not been accepted by later writers such as Mathew (1989), although the latter kept Hermodactylus as a distinct genus, to include Hermodactylus tuberosus, now returned to Hermodactyloides as Iris tuberosa.[4]
Rodionenko also reduced the number of sections in subgenus Iris, from six to two, depending on the presence (Hexapogon) or absence (Iris) of arils on the seeds, referred to as arilate or nonarilate. Taylor (1976) provides arguments for not including all arilate species in Hexapogon.[4]
In general, modern classifications usually recognise six subgenera, of which five are restricted to the Old World; the sixth (subgenus Limniris) has a Holarctic distribution. The two largest subgenera are further divided into sections.
§Subgeneric division[edit]
§Subgenera[edit]
- Iris (Bearded rhizomatous irises)
- Limniris (Beardless rhizomatous irises)
- Xiphium (Smooth-bulbed bulbous irises: Formerly genus Xiphion)
- Nepalensis (Bulbous irises: Formerly genus Junopsis)
- Scorpiris (Smooth-bulbed bulbous irises: Formerly genus Juno)
- Hermodactyloides (Reticulate-bulbed bulbous irises: Formerly genus Iridodictyum)
§Sections, series and species[edit]
§Distribution and habitat[edit]
Nearly all species are found in temperate Northern hemisphere zones, particularly from Eurasia to Asia. Although diverse in ecology, Iris is predominantly found in dry, semi-desert, or colder rocky mountainous areas,[4] other habitats include grassy slopes, meadowlands and riverbanks.
§Cultivation[edit]
Irises are extensively grown as ornamental plants in home and botanical gardens. Presby Memorial Iris Gardens in New Jersey, for example, is a living iris museum with over 10,000 plants, while in Europe the most famous iris garden is arguably the Giardino dell'Iris in Florence (Italy) which every year hosts one of the most famous iris breeders' competitions in the world. Irises, especially the multitude of bearded types, feature regularly in shows such as the Chelsea Flower Show. Irises grow in any good free garden soil, the smaller and more delicate species needing only the aid of turf ingredients, either peat or loam, to keep it light and open in texture. The earliest to bloom are species like I. junonia and I. reichenbachii, which flower as early as February and March (Northern Hemisphere), followed by the dwarf forms of I. pumila which blossom in Spring, followed in early Summer by most of the tall bearded varietis, such as the German Iris and its variety florentina, Sweet Iris, Hungarian Iris, Lemon-yellow Iris (I. flavescens), Iris sambucina, I. amoena, and their natural and horticultural hybrids such as those described under names like I. neglecta or I. squalens and best united under I. × lurida.
§Bearded rhizomatous irises[edit]
The most commonly found garden iris is the bearded German Iris (I. germanica) and its numerous cultivars. Various wild forms and naturally occurring hybrids of the Sweet iris (I. pallida) and the Hungarian iris (I. variegata) form the basis of almost all modern hybrid bearded irises. Median forms of bearded iris (intermediate bearded, or IB; miniature tall bearded, or MTB; etc.) are derived from crosses between tall and dwarf varieties.
The bearded irises are easy to cultivate and propagate, and have become very popular in gardens. A small selection is usually held by garden centres at appropriate times during the season, but there are thousands of cultivars available from specialist suppliers. They are best planted as bare root plants in late summer, in a sunny open position with the rhizome visible on the surface of the soil and facing the sun. They should be divided in summer every two or three years, when the clumps become congested.
A truly red bearded iris, like a truly blue rose, remains an unattained goal despite frequent hybridizing and selection. There are species and selections, most notably based on the beardless rhizomatous Copper iris (I. fulva), which have a relatively pure red color. However, getting this color into a modern bearded iris breed has proven very difficult, and thus, the vast majority of irises are in the purple and blue range of the color spectrum, with yellow, pink, orange and white breeds also available.
The following is a selection of bearded irises which have gained the Royal Horticultural Society's Award of Garden Merit:-
|
§Oncocyclus section[edit]
This section contains the cushion irises or royal irises, a group of plants noted for their large, strongly marked flowers. Between 30 and 60 species are classified in this section, depending on the authority. Compared with other irises the cushion varieties are scantily furnished with narrow sickle-shaped leaves and the flowers are usually borne singly on the stalks; they are often very dark and in some almost blackish. The cushion irises are somewhat fastidious growers, and to be successful with them they must be planted rather shallow in very gritty well-drained soil. They should not be disturbed in the autumn, and after the leaves have withered the roots should be protected from heavy rains until growth starts again naturally.
§Regelia section[edit]
This section, closely allied to the cushion irises, includes several garden hybrids with species in section Oncocyclus, known as Regelio-cyclus irises. They are best planted in September or October in warm sunny positions, the rhizomes being lifted the following July after the leaves have withered.
§Beardless rhizomatous (subgenus Limniris) irises[edit]
Beardless rhizomatous iris types commonly found in the garden are the Siberian iris (I. sibirica) and its hybrids, and the Japanese Iris (I. ensata) and its hybrids. "Japanese Iris" is also a catch-all term for the Japanese iris proper (hanashōbu), the Blood iris (I. sanguinea, ayame) and the Rabbit-ear iris (I. laevigata, kakitsubata). I. unguicularis is a late-winter-flowering species from Algeria, with sky-blue flowers blotched with yellow, produced from Winter to Spring. Yet another beardless rhizomatous iris popular in gardening is I. ruthenica, which has much the same requirements and characteristics as the tall bearded irises.
§Reticulate-bulbed (subgenus Hermodactyloides) irises[edit]
Reticulate irises with their characteristic bulbs, including the yellow I. danfordiae, and the various blue-purple I. histrioides and I. reticulata, flower as early as February and March. These reticulate-bulbed irises are miniatures and popular spring bulbs, being one of the first to bloom in the garden. Many of the smaller species of bulbous iris, being liable to perish from excess of moisture, should have a well-drained bed of good but porous soil made up for them, in some sunny spot, and in winter should be protected by a covering of half-decayed leaves or fresh cocos-fibre refuse.
§Gallery[edit]
-
Iris atropurpurea, one of the dark-flowered Oncocyclus bearded irises
-
Iris unguicularis flower
-
Iris pseudacorus in Cheshire in England
-
Iris Sharpshooter in the Real Jardín Botánico de Madrid, Spain
§Aromatic rhizomes[edit]
Rhizomes of the German Iris (I. germanica) and Sweet Iris (I. pallida) are traded as orris root and are used in perfume and medicine, though more common in ancient times than today. Today Iris essential oil (absolute) from flowers are sometimes used in aromatherapy as sedative medicines. The dried rhizomes are also given whole to babies to help in teething. Gin brands such as Bombay Sapphire and Magellan Gin use orris root and sometimes iris flowers for flavor and color.
For orris root production, iris rhizomes are harvested, dried, and aged for up to 5 years. In this time, the fats and oils inside the roots undergo degradation and oxidation, which produces many fragrant compounds that are valuable in perfumery. The scent is said to be similar to violets. The aged rhizomes are steam-distilled which produces a thick oily compound, known in the perfume industry as "iris butter" or orris oil.
Iris rhizomes also contain notable amounts of terpenes, and organic acids such as ascorbic acid, myristic acid, tridecylenic acid and undecylenic acid. Iris rhizomes can be toxic. Larger blue flag (I. versicolor) and other species often grown in gardens and widely hybridized contain elevated amounts of the toxic glycoside iridin. These rhizomes can cause nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and/or skin irritation, but poisonings are not normally fatal. Irises should only be used medicinally under professional guidance.
§Water purification[edit]
In water purification, Yellow Iris (I. pseudacorus) is used. The roots are usually planted in a substrate (e.g. lava-stone) in a reedbed-setup. The roots then improve water quality by consuming nutrient pollutants, such as from agricultural runoff.
§In art and symbolism[edit]
An iris – species unspecified – is one of the state flowers of Tennessee. Tradition holds that the particular iris symbolizing Tennessee is a purple cultivar, to go alongside the wild-growing Purple Passion Flower (Passiflora incarnata) which is the state's other floral emblem. Greeneville, Tennessee is home to the annual Iris Festival celebrating the Iris, local customs, and culture.[16]
The artist George Gessert has specialised in breeding irises.[17]
The artist Vincent van Gogh painted several famous pictures of irises.[18]
The American artist, Joseph Mason — a great friend of John James Audubon — painted a precise image of what was then known as the Lousianna Flag or Copper Iris (Iris fulva) to which Audubon subsequently added two Northern Paraula birds (parula americana) for inclusion as Plate 15 in his Birds of America.
The artist Philip Hermogenes Calderon painted an iris in his 1856 work Broken Vows; he followed the principles of the Pre-Raphaelite Brotherhood. An ancient belief is that the iris serves as a warning to be heeded, as it was named for the messenger of Olympus. It also conveys images of lost love and silent grief, for young girls were led into the afterlife by Iris. Broken Vows was accompanied with poetry by Henry Wadsworth Longfellow when it was first exhibited.[19]
The fleur-de-lis, a stylized iris, first occurs in its modern use as the emblem of the House of Capet. The fleur-de-lis has been associated with France as Louis VII adopted it as a symbol in the 12th Century. The yellow fleur-de-lis reflects the Yellow Iris (I. pseudacorus), common in Western Europe. Contemporary uses can be seen in the Quebec flag and the logo of the New Orleans Saints professional football team, and on the flag of Saint Louis, Missouri.
The red fleur-de-lis in the coat-of-arms of Florence (Italy) descends from the white iris which is native to Florence and which grew even in its city walls. This white iris, displayed against a red background, became the symbol of Florence until the Medici family, to signal a change in political power, reversed the colors making the white one red and setting in motion a centuries-long breeding program to hybridize a red iris.
Furthermore, the fleur-de-lis is the almost-universal symbol of Scouting and one of the symbols adopted by the sorority, Kappa Kappa Gamma.
A stylized Yellow Iris is the symbol of Brussels, since historically, the important Saint Gaugericus Island was carpeted in them.[20] The iris symbol is now the sole feature on the flag of the Brussels-Capital Region.
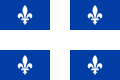
The provincial flower of Québec (Canada) is the Harlequin Blueflag (I. versicolor), called iris versicolore in French.
-
Philip Hermogenes Calderon's Broken Vows with the iris at lower left
-
Coat-of-arms of the House of Capet
§See also[edit]
§References[edit]
- ^ "WCSP: Iris". World Checklist of Selected Plant Families. Retrieved 2 June 2014.
- ^ "Iris". Pacific Bulb Society. 2011-11-26. Retrieved 2012-03-03.
- ^ Manning, John; Goldblatt, Peter (2008). The Iris Family: Natural History & Classification. Portland, Oregon: Timber Press. pp. 200–204. ISBN 0-88192-897-6.
- ^ a b c d Rina Kamenetsky, Hiroshi Okubo, ed. (2012). "Iridaceae". Ornamental Geophytes: From Basic Science to Sustainable Production. CRC Press. p. 24. ISBN 1-4398-4924-2.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Alizes'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Bumblebee Deelite'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Early Light'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Jane Phillips'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Langport Wren'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Maui Moonlight'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Orinoco Flow'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Raspberry Blush'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Sarah Taylor'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Thornbird'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "RHS Plant Selector - Iris 'Titan's Glory'". Royal Horticultural Society. Retrieved 20 May 2013.
- ^ "18th Annual Iris Festival". Greenecountypartnership.com. Retrieved 2012-03-03.
- ^ West [2008]
- ^ Pioch (2002)
- ^ Mancoff (2003): p.6,16
- ^ Chancery of the Prime Minister, Kingdom of Belgium [2007]
§Bibliography[edit]
- Chancery of the Prime Minister, Kingdom of Belgium [2007]: Brussels Town Hall. Retrieved November 11, 2007.
- Rina Kamenetsky, Hiroshi Okubo, ed. (2012). "Iridaceae". Ornamental Geophytes: From Basic Science to Sustainable Production. CRC Press. p. 24. ISBN 1-4398-4924-2.
- Mancoff, Debra N. (2003): Flora Symbolica: Flowers in Pre-Raphaelite Art. Prestel Publishing, New York, USA. ISBN 3-7913-2851-4.
- Pioch, Nicolas (2002): Gogh, Vincent van: Irises. Bersion of 2002-AUG-19. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
- Species Group of the British Iris Society (1996): A Guide to Species Irises: Their Identification and Cultivation; Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. ISBN 0-521-44074-2.
- West, Ruth [2008]: George Gessert. Retrieved December 10, 2008.
§Taxonomy[edit]
- American Iris Society. Systematic Treatment of the Genus Iris by Baker. 2012
- Dykes, W. R. (1913): The Genus Iris. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. ISBN 0486230376
- Harris, Gwenda. CLASSIFICATION OF IRISES. New Zealand Iris Society 2011
- Brian Mathew. The Iris. Batsford, London 1989
- George Hill Mathewson Lawrence. A Reclassification of the Genus Iris. Gentes Herb 8:346-371 1953
- Rodionenko, G. I.: The Genus Iris L. (Questions of Morphology, Biology, Evolution and Systematics). British Iris Society, London 1987. (trans.)
- Taylor, J.J. 1976. A reclassification of Iris species bearing arillate seeds. Proceedings of the Biological Society, Washington. 89: 411-420.
- Wilson, Carol. Phylogeny of the genus Iris based on DNA sequence data. Rancho Santa Ana 2004
§External links[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Iris (Iridaceae). |
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Iris cultivars by alphabet. |
- Joseph Mason's painting - Copper Iris Copper Iris / Louisiana Flag (Iris cuprea) from John James Audubon's Birds of America
- Flora of North America: Iris
- Flora of China: Iris
- Flora of Pakistan: Iris
- Flora of Nepal: Iris
- A web site devoted to Irises, by David Payne-Joyce; includes plates from Dykes (1913).
- The American Iris Society
- Historic Iris Preservation Society
- Iris listings at Wild Flowers of Israel
- Iris in Art and Culture
- Gouvernement du Québec Emblèmes du Québec - Iris versicolor (French)
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | Wikipedia |
| Source | http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Iris_(plant)&oldid=650291100 |
Subgenus Iris is one subgenus of Iris, The genus was originally clasified by Carl Linnaeus, but then further organised by Brian Mathew between 1981 and 1987.[1]
It has been divided into six sections; Bearded irises (or pogon irises), Psammiris, Oncocylclus, Regelia, Hexapogon and Pseudoregelia.
Contents
Section Bearded irises (or pogon irises)[edit]
This is the largest section of the subgenus. Most irises come from Southern or eastern Europe.[1] Note 'pogon' refers to the Greek word for beard.[2] It has several species of iris including;
|
|
It also includes thousands of hybrids which have been divided into various height categories.[3]
- MDB - Miniature Dward bearded
- SDB - Standard Dwarf bearded
- IB - Intermediate bearded
- BB - Border bearded
- MTB - Miniature Tall bearded
- TB - Tall bearded
Psammiris[edit]
This section of irises was first described by Spach. Irises from Russia and Northwest china. Mostly rhizomatous, and flowering in late spring.[1] Note psammos derives from the Greek word for sand.[2]
- Iris bloudowii Bunge.
- Iris curvifolia Zhao[4]
- Iris humilis Georgi
- Iris kamelinii Alexeeva
- Iris mandschurica Maxim.
- Iris potaninii Maxim.
- Iris vorobievii N.S.Pavlova
Oncocylus[edit]
All irises are rhizomatous perennials. They also generally need rich soils that drain easy and are in full sun. Most also prefer a dry period after flowering.[5] Irises mostly from Turkey, Caucasus and Iran. The flowers usually only have one flower. Some of these species have been bred with bearded irises to create unique colours and markings.[1] Oncocyclus is a Greek word, with onco meaning mass, or bulk, and cyclus meaning circle.[6]
- Iris acutiloba C.A.Mey. (including I. ewbankiana
- Iris assadiana Chaudhary, Kirkw. & C.Weymolauth
- Iris aurantiaca Dinsmore
- Iris atrofusca Bak.
- Iris atropurpurea Bak.
- Iris barnumae Bak. & Fost.
- Iris bismarckiana Reg. – Nazareth Iris
- Iris bostrensis Mouterde
- Iris camillae Grossh.
- Iris gatesii Foster
- Iris haynei (Bak.) Mallet. – Gilboa Iris
- Iris hermona Dinsmore – Hermon Iris
- Iris iberica Hoffm.
- Iris iberica subsp. elegantissima (Sosn.) Fed. & Takht.
- Iris iberica subsp. lycotis (Woronow) Takht.
- Iris kirkwoodi (including I. calcarea)
- Iris lortetii Barbey ex Boiss.
- Iris mariae Barbey.
- Iris meda Stapf
- Iris paradoxa Steven
- Iris petrana Dinsm.
- Iris polakii Stapf
- Iris sari Schott ex Bak.
- Iris sofarana Fost.
- Iris susiana L. – Mourning Iris
Regelia[edit]
Mostly from the mountainous regions of Iran, Afghanistan and the Altai Mountains.[7] Most irises have a stem that has 2 flowers.[1] It was named in 1904 by Robert Lynch in his book 'The Book of The Iris' after Dr Regel.[8]
- Iris afghanica Wend
- Iris darwasica Regel
- Iris heweri Grey-Wilson & B. Mathew
- Iris hoogiana Dykes
- Iris kuschkensis Grey-Wilson & B. Mathew
- Iris lineata Foster ex Regel
- Iris korolkowii Regel
- Iris stolonifera Maxim.
Hybrids of Regelia irises and Oncocyclus irises are known as 'Regelicyclous'.[9]
Hexapogon[edit]
Mostly from the desert area of Central Asia, Iran and Afghanistan. Most irises have beards on the falls and standards.[1] Note 'hexa' refers to the number 6 and 'pogon' refers to the Greek word for beard.[2]
- Iris falcifolia Bunge
- Iris longiscapa Ledeb.
Pseudoregelia[edit]
Mostly from the mountainous regions of Eastern Asia. Most irises have flowers that have blothes or colour spots on.[1]
- Iris goniocarpa Bak.
- Iris hookeriana Fost.
- Iris ivanovae Doronkin
- Iris kamaonensis Wall.
- Iris leptophyll Lingelsheim
- Iris sikkimensis Dykes
- Iris tigrida Bunge ex Ledeb.
References[edit]
- ^ a b c d e f g Stebbings, Geoff (1997). The Gardener's Guide to Growing Irises. Newton Abbot: David and Charles. p. 18. ISBN 0715305395.
- ^ a b c Stearn, William (1972). A Gardenerer's Dictionary of Plant Names. London: Cassell. p. 211. ISBN 0304937215.
|accessdate=requires|url=(help) - ^ Morris, Jim (2011). "Bearded Iris Classifications". www.irises.org (American Iris Society). Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ British Iris Society A Guide to Species Irises: Their Identification and Cultivation, p. 60, at Google Books
- ^ Christopher Brickell RHS Encyclopedia of Plants and Flowers, p. 521, at Google Books
- ^ Saad, Layla; Khuri, Sawsan (4 August 2003). "Hanging in There by a Fall – The Oncocyclus Irises of Lebanon" (pdf). orbi.ulg.ac.be. Retrieved 23 July 2014.
- ^ Cassidy, G.E.; Linnegar, S. (1987). Growing Irises (Revised ed.). Bromley: Christopher Helm. pp. 144–145. ISBN 0-88192-089-4.
|accessdate=requires|url=(help) - ^ "The book of the iris, by R. Irwin Lynch". www.biodiversitylibrary.org. p. 116. Retrieved 24 July 2014.
- ^ Christopher Brickell RHS Encyclopedia of Plants and Flowers, p. 610, at Google Books
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | Wikipedia |
| Source | http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Iris_subg._Iris&oldid=648899539 |
Tigridia pavonia is the best-known species from the genus Tigridia, in the Iridaceae family. Common names include jockey's cap lily,[3] Mexican shellflower[4] peacock flower,[4] and tiger flower.[4] The species is widespread across much of Mexico as well as Guatemala, El Salvador, and Honduras. The species is also considered naturalized in Ecuador and Peru.[4][5]
It is very popular as an ornamental plant among lovers of interesting flowers. The blooms come in a variety of colours. They open early in the morning and are already closed around 5 P.M. when dusk begins to fall. Every day a different bloom is opened. The plants that are grown from seeds bloom in the first year after they are sowed.
References[edit]
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Tigridia pavonia. |
- ^ "The International Plant Names Index, entry for publication Les Liliacées". which states that the author of the plant names is Redouté and not de Candolle
- ^ "The Plant List: A Working List of All Plant Species". Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ Books, M.; Limited, M.B.P. (2004). Growing Bulbs. Murdoch Books. ISBN 9781740455206.
- ^ a b c d "USDA GRIN Taxonomy". Retrieved 16 January 2014.
- ^ Kew World Checklist of Selected Plant Families
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | Wikipedia |
| Source | http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Tigridia_pavonia&oldid=623818367 |
Chile Central
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | Pablo Gutierrez, IABIN |
| Source | No source database. |
Isoneotype for Ferraria pavonia L.
Catalog Number: US 933901
Collection: Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History, Department of Botany
Verification Degree: ; Status verified from secondary sources
Preparation: Pressed specimen
Collector(s): C. G. Pringle
Year Collected: 1896
Locality: Valley near Tula., Hidalgo, Mexico, North America
Elevation (m): 2073
- Isoneotype: Linnaeus, C. 1781. Suppl. Pl. 407.; Molseed, E. W. 1970. Univ. Calif. Publ. Bot. 54: 37.
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | This image was obtained from the Smithsonian Institution. Unless otherwise noted, this image or its contents may be protected by international copyright laws. |
| Source | http://collections.mnh.si.edu/search/botany/?irn=10080593 |
Isoneotype for Ferraria pavonia L.
Catalog Number: US 960270
Collection: Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History, Department of Botany
Verification Degree: ; Status verified from secondary sources
Preparation: Pressed specimen
Collector(s): C. G. Pringle
Year Collected: 1896
Locality: Valley near Tula., Hidalgo, Mexico, North America
Elevation (m): 2073
- Isoneotype: Linnaeus, C. 1781. Suppl. Pl. 407.; Molseed, E. W. 1970. Univ. Calif. Publ. Bot. 54: 37.
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | This image was obtained from the Smithsonian Institution. Unless otherwise noted, this image or its contents may be protected by international copyright laws. |
| Source | http://collections.mnh.si.edu/search/botany/?irn=10080592 |
Neotype for Ferraria pavonia L.
Catalog Number: US 287734
Collection: Smithsonian Institution, National Museum of Natural History, Department of Botany
Verification Degree: ; Status verified from secondary sources
Preparation: Pressed specimen
Collector(s): C. G. Pringle
Year Collected: 1896
Locality: Valley near Tula., Hidalgo, Mexico, North America
Elevation (m): 2073
- Neotype: Linnaeus, C. 1781. Suppl. Pl. 407.; Molseed, E. W. 1970. Univ. Calif. Publ. Bot. 54: 37.
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | This image was obtained from the Smithsonian Institution. Unless otherwise noted, this image or its contents may be protected by international copyright laws. |
| Source | http://collections.mnh.si.edu/search/botany/?irn=10080591 |
Foodplant / pathogen
Ditylenchus destructor infects and damages live, discoloured leaf of Tigridia pavonia
Other: minor host/prey
| This article does not cite any references or sources. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. (September 2011) |
Iris a genus of praying mantis.
Species:
- Iris coeca
- Iris deserti
- Iris fasciata
- Iris insolita
- Iris minima
- Iris nana
- Iris narzykulovi
- Iris oratoria (Mediterranean Mantis)
- Iris orientalis
- Iris persa
- Iris pitcheri
- Iris polystictica
- Iris senegalensis
- Iris splendida
See also[edit]
References[edit]
| This Mantodea-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
| License | http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/ |
| Rights holder/Author | Wikipedia |
| Source | http://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Iris_(insect)&oldid=582769985 |